Specification for Thruster
1. Overview
- This class simulates a thruster and contains functions for it.
1. functions
- By setting the thruster valve open and close, thruster torque and force are generated.
- The thruster model includes the magnitude and directional errors in the ini file.
- According to the thruster output, users can set the thrust duty to the value between 0 and 1.
2. files
simple_thruster.cpp,simple_thruster.hpp- Definitions and declarations of the class
thruster.ini- Parameters for a/multiple thruster(s)
plot_simple_thruster.py: An example of a Python script to plot simple thruster output
3. how to use
- Set the parameters written in
thruster.ini.- Users can set multiple thrusters.
- Create an instance by
SimpleThrusterfunction. - Add
calc_thrustfunction toGenerateForce_b()inSatComponentsclass andcalc_torquefunction toGenerateTorque_b()inSatComponentsclasscalc_torquefunction requires a position of the spacecraft's mass center as an argument.
- When a thruster is open, set the duty to 1 by
set_duty(1)function.- Users can set duty to the value between 0 and 1.
2. Explanation of Algorithm
1. Thrust
1. overview
- Thrust magnitude is a scalar value of thrust.
- Thrust contains the magnitude and direction errors according to the ini file setting.
- Thrust magnitude calculation considers the duty of thruster. If the thruster valve is closed, the thrust magnitude is 0.
2. input and output
- input
- Thruster duty ratio
- Maximum thrust magnitude
thrust_magnitude_N - Thrust direction
thruster_direction_b - Thrust magnitude error
thrust_error_standard_deviation_N - Thrust direction error
direction_error_standard_deviation_deg
- output
- Thrust magnitude and direction
3. algorithms
Thrust magnitude can be calculated as follows:
\[ F_{thrust} = \epsilon * F_{max} + n_{f} \]
where $F_{thrust}$ is thrust magnitude, $\epsilon$ is the duty of thruster, $F_{max}$ is the maximum thrust magnitude, and $n_{f}$ is the error of thrust magnitude.
Thrust direction can be calculated as follows:
\[ \boldsymbol{d}_{err} = \boldsymbol{q}(\boldsymbol{d}_{true},n) * \boldsymbol{d}x \] \[ \boldsymbol{d}_{thrust} = \boldsymbol{q}(\boldsymbol{d}_{err},n{d}) * \boldsymbol{d}_{true} \]
where
- $\boldsymbol{d}_{true}$ is the thrust vector without errors
- $n$ is the random angles to rotate the direction of error $\boldsymbol{d}_{err}$
- $\boldsymbol{d}_{x}$ is the vector which is not equal to $\boldsymbol{d}_{true}$
- $n_d$ is the directional error
- $\boldsymbol{d}_{thrust}$ is the thrust vector with errors
- $\boldsymbol{q}(\boldsymbol{d},n)$ is the quaternion which has the rotation axis $\boldsymbol{d}$ and the rotation angle $n$ .
Thrust can be calculated as follows:
\[ \boldsymbol{F}_{thrust} = F_{thrust} * \boldsymbol{d}_{thrust} \]
where $\boldsymbol{F}_{thrust}$ is thrust.
2. Torque
1. overview
- Torque by thruster is calculated from the thrust vector and the vector between the center of mass of the spacecraft and thruster.
2. input and output
- input
- Thruster position
thruster_position_b_m - Mass center of spacecraft
- Thrust magnitude and direction
- Thruster position
- output
- Torque
3. algorithms
Torque by the thruster can be calculated as follows:
\[ \boldsymbol{T}_{thrust} = (\boldsymbol{v}_{thruster}-\boldsymbol{v}_{SC}) \times \boldsymbol{F}_{thrust} \]
where
- $\boldsymbol{T}_{thrust}$ is torque by the thruster
- $\boldsymbol{v}_{thruster}$ is thruster position
- $\boldsymbol{v}_{SC}$ is the mass center of spacecraft.
3. Results of verifications
1. Case1
-
input
- Position
thruster_position_b_m: [0m, 0m, 0.1m] - Direction
thruster_direction_b: [0, 0, 1] - Thrust magnitude
thrust_magnitude_N: 0.001N - Thrust magnitude error
thrust_error_standard_deviation_N: 0.0N - Thrust direction error
direction_error_standard_deviation_deg: 0.0deg - Simulation time: 100sec
- Position
-
result
-
Force Mean: [0,0,0.001] N
-
Force Std Dev: [0,0,0] N
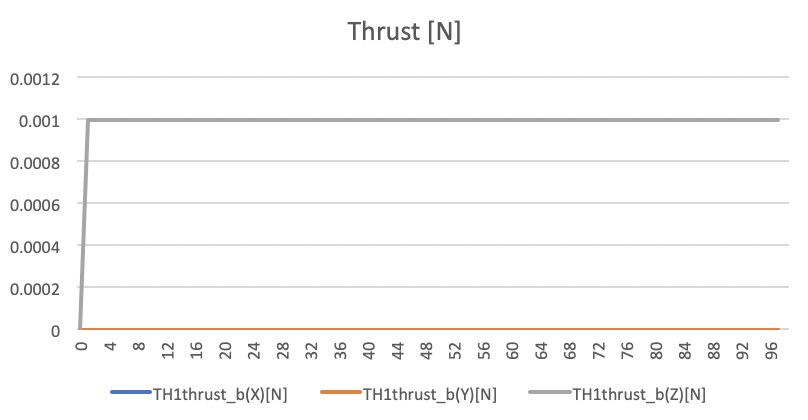
Thrust force values in N unit. -
Torque Mean: [0,0,0] Nm
-
Torque Std Dev: [0,0,0] Nm
Thrust torque values in Nm unit.
-
2. Case2
- input
- Position
thruster_position_b_m: [0, 0, 0.1] m - Direction
thruster_direction_b: [0, 0, 1] - Thrust magnitude
thrust_magnitude_N: 0.001N - Thrust magnitude error
thrust_error_standard_deviation_N: 0.00001N - Thrust direction error
direction_error_standard_deviation_deg: 0.0deg - Simulation time: 100sec
- Position
- result
-
Force Mean: [0,0,0.999611e-3] N
-
Force Std Dev: [0,0,1.09804e-5] N
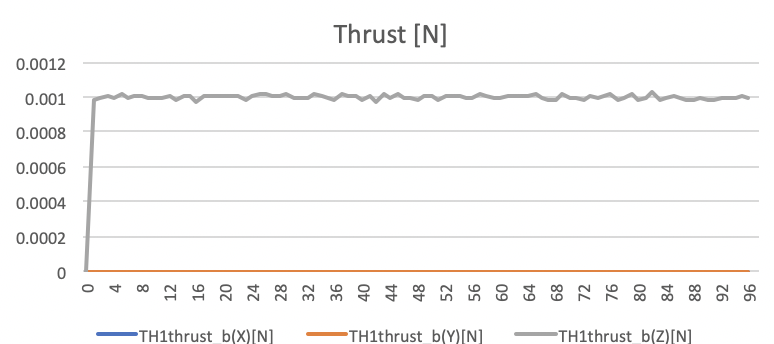
Thrust force values in N unit. -
Torque Mean: [0,0,0] Nm
-
Torque Std Dev: [0,0,0] Nm
Thrust torque values in Nm unit.
-
3. Case3
- input
- Position
thruster_position_b_m: [0, 0, 0.1] m - Direction
thruster_direction_b: [0, 0, 1] - Thrust magnitude
thrust_magnitude_N: 0.001N - Thrust magnitude error
thrust_error_standard_deviation_N: 0.0N - Thrust direction error
direction_error_standard_deviation_deg: 10.0deg - Simulation time: 100sec
- Position
- result
-
Force Mean: [-4.93e-6, -1.04e-5, 0.9834e-3] N
-
Force Std Dev: [1.0e-4, 9.79e-5, 1.216e-5] N
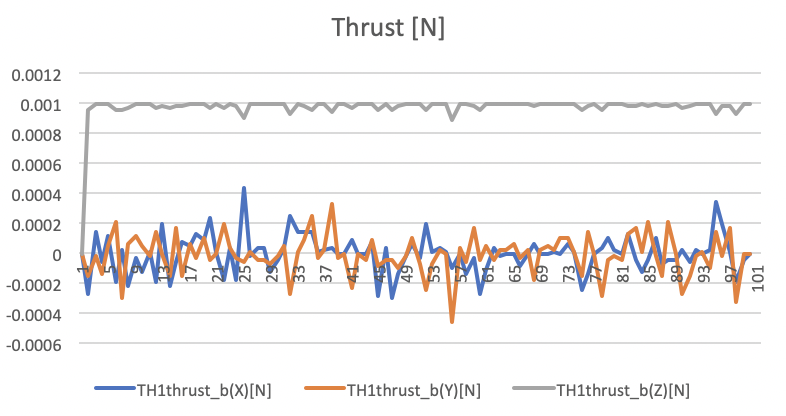
Thrust force values in N unit. -
Torque Mean: [1.04e-6,-4.94e-7,0] Nm
-
Torque Std Dev: [1.29e-5, 1.26e-5, 0] Nm
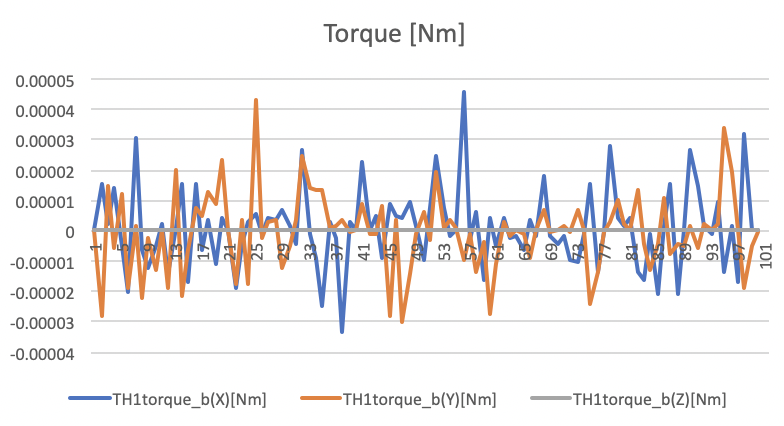
Thrust torque values in Nm unit.
-
4. Case4
- input
- Position
thruster_position_b_m: [0, 0.1, 0] m - Direction
thruster_direction_b: [0, 0, 1] - Thrust magnitude
thrust_magnitude_N: 0.001N - Thrust magnitude error
thrust_error_standard_deviation_N: 0.0N - Thrust direction error
direction_error_standard_deviation_deg: 0.0deg - Simulation time: 100sec
- Position
- result
-
Force Mean: [0,0,0.001] N
-
Force Std Dev: [0,0,0] N
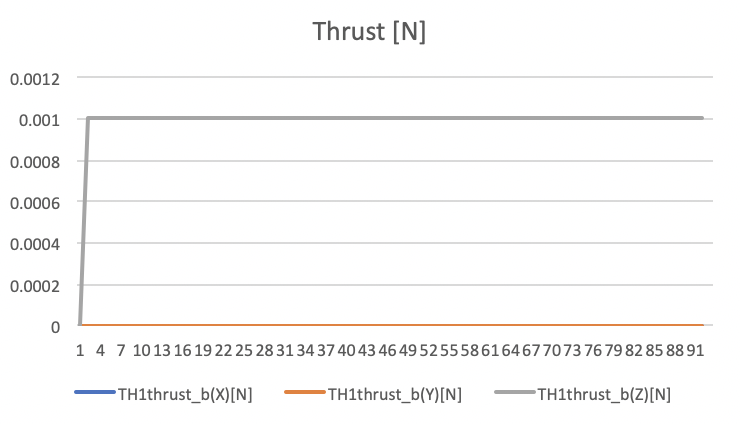
Thrust force values in N unit. -
Torque Mean: [0.0001,0,0] Nm
-
Torque Std Dev: [0,0,0] Nm
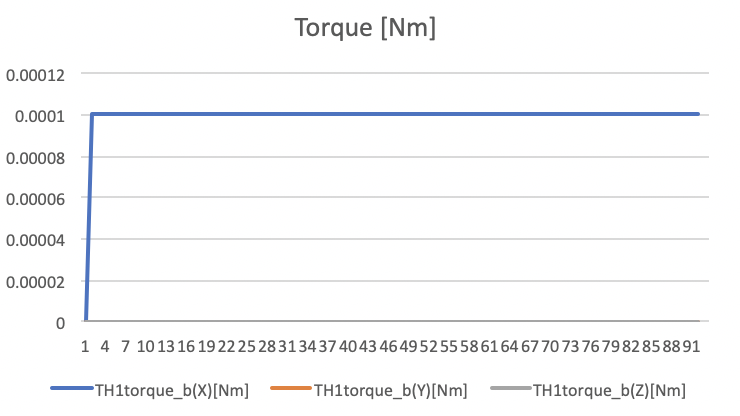
Thrust torque values in Nm unit.
-